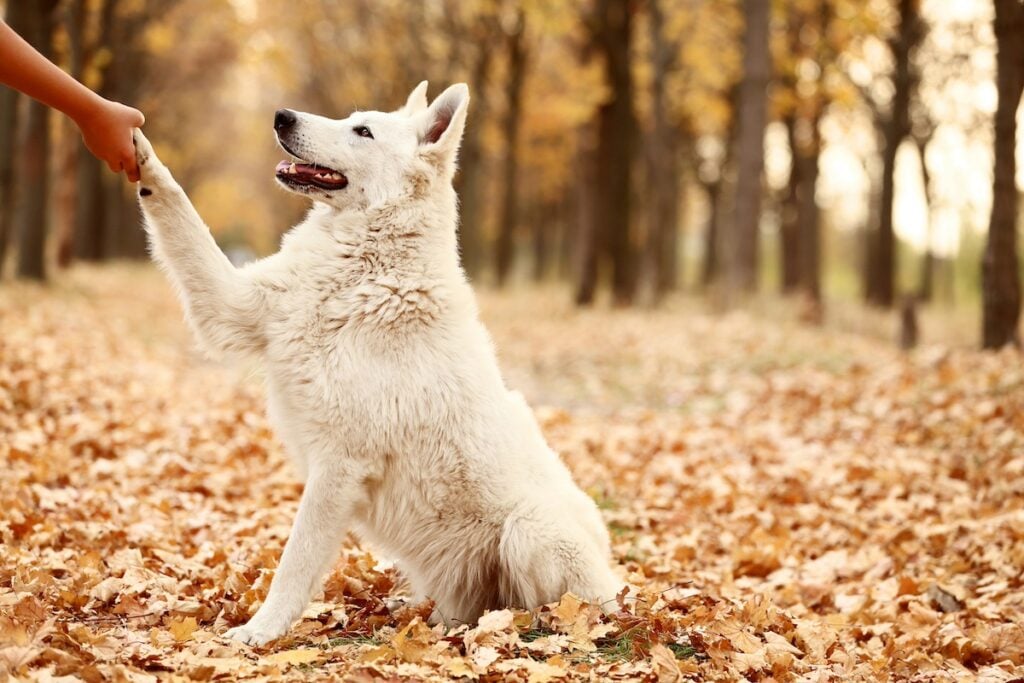
If you pay attention when your dog reaches for a toy or gives you their paw, you might just notice that they tend to prefer using one paw over the other. It turns out that, just as humans are right or left-handed, most dogs also show a dominant paw. There are some interesting similarities and differences between human and dog ‘handedness’.
It is known that in dogs and humans (along with many other animals and insects) the right and left hemispheres of the brain process information differently and are responsible for different behaviors. This difference, known as lateralization, seems to make the brain more efficient as the two hemispheres of the brain can focus on two different tasks. The right hemisphere of the brain is responsible for the left side of the body, and the left hemisphere controls the right side.
99% of humans are either right or left-handed, instead of ambidextrous (using both hands equally), and the majority of dogs also show a preference for their right or left paw, rather than having no preference. However, unlike humans, where only 10% of people are left-handed, the split between right and left paw dominant dogs is nearly even.
In 2021, researchers from Lincoln University in the U.K. conducted a large survey of almost 18,000 dogs to see if the sex and age of dogs influenced their dominant pawedness. Interestingly, almost 61% of female dogs were right paw dominant, compared to 56% of the males. The researchers also found that elderly dogs were more likely to be right pawed than younger dogs. Older dogs also seemed much more entrenched in the use of their dominant paw while younger dogs were more fluid in which paw they chose.
Table of Contents:
Is Your Dog a Rightie or a Leftie?
Researchers have agreed on a few tests that seem reliable to determine dog paw preference. These are easy to do and fun to try at home to see if your dog shows a leaning toward a particular paw. One test is the ‘step off’ test. Watch which leg the dog uses to take their first step from standing still. If they generally step forward with the same foot, that is their dominant side. Another is known as the Kong test. If a dog is given a stuffed Kong, the paw they repeatedly use to stabilize the Kong while getting the food out is their dominant paw. Paw dominance can be shown in other everyday behaviors as well; some dogs always circle in the same direction as they are settling to lie down, and others will use the same dominant paw to reach for a toy or offer a paw to shake. Once you start looking for patterns in which paw your dog prefers, it should become clear that they either don’t display paw dominance, or they reliably choose one side.
What Does Dominant Paw Difference Show?
Studies have shown that the right and left hemispheres of the brain are responsible for processing emotions (along with directing the actions on the opposite side of the body). Researchers determined that positive emotions are processed in the left hemisphere with actions on the right side of the body, and negative emotions are processed in the right hemisphere and shown through the left side of the body.
Knowing this has allowed people to assess dog behavior in order to help to determine the dog’s emotional state of mind. For example, dogs will wag their tails more to the right when they see something familiar that they are excited about and will wag more to the left if someone unfamiliar is approaching them.
Researchers also determined that dogs react to unpleasant noises by using their left ear more than their right ear. Studies have also found that dogs without a specific paw preference are the most sensitive to unpleasant noises and display more noise related fear behaviors.
Potential guide dogs who are right pawed have more success through the training process and become certified guide dogs more frequently than dogs who show left paw dominance or do not favor either paw. It is thought that right paw dominance reflects a less reactive personality with fewer fear behaviors, which allows those dogs to be more successful as service dogs.
And, while there are many factors influencing the level of aggression in dogs, the early research seems to establish a link between dogs who display aggression and those who are either left paw dominant or do not favor a paw. Left paw dominant dogs might be seen to view the world in a more pessimistic way, which could put them at greater risk of poor social outcomes.
The Bottom Line
We know so much about our fur family, from their favorite toys and places to cuddle up to the way they love to have their ears scratched. Knowing which paw they favor can give us added insight into their personality and the way they view the world. Consider which paw they use to reach for toys or use to hold down a Kong while taking treats out. As you start to pay more attention to which paw your pup favors, you might be able to see a pattern showing their paw dominance. While some paw use can depend on the activity—using the closer foot to scratch an itch, for example, most dogs will use one side of their body more than the other. If they offer you a paw or if your male dog lifts one leg more than the other to urinate, they are probably showing you their dominant paw. Your dog’s perspective on the world can also be related to their use of a dominant paw. If your dog is right pawed, they might view new people and situations as potential friends and approach life with a positive outlook, while left pawed dogs could require a more supportive relationship to help them face their worries.
Sources:
https://www.akc.org/expert-advice/lifestyle/dog-right-or-left-pawed/
https://www.amcny.org/blog/2021/08/11/are-dogs-left-handed-and-cats-right-handed/